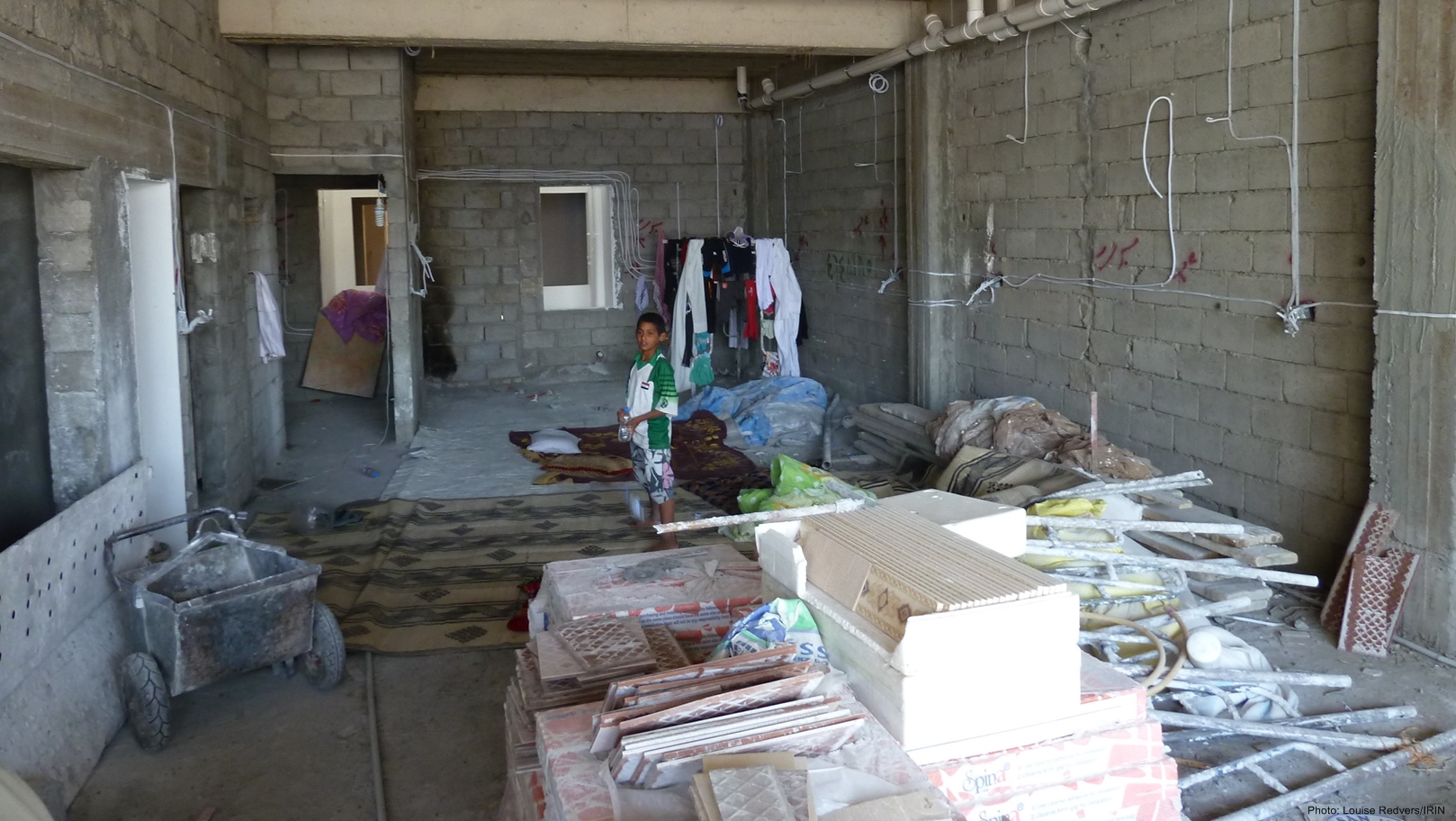
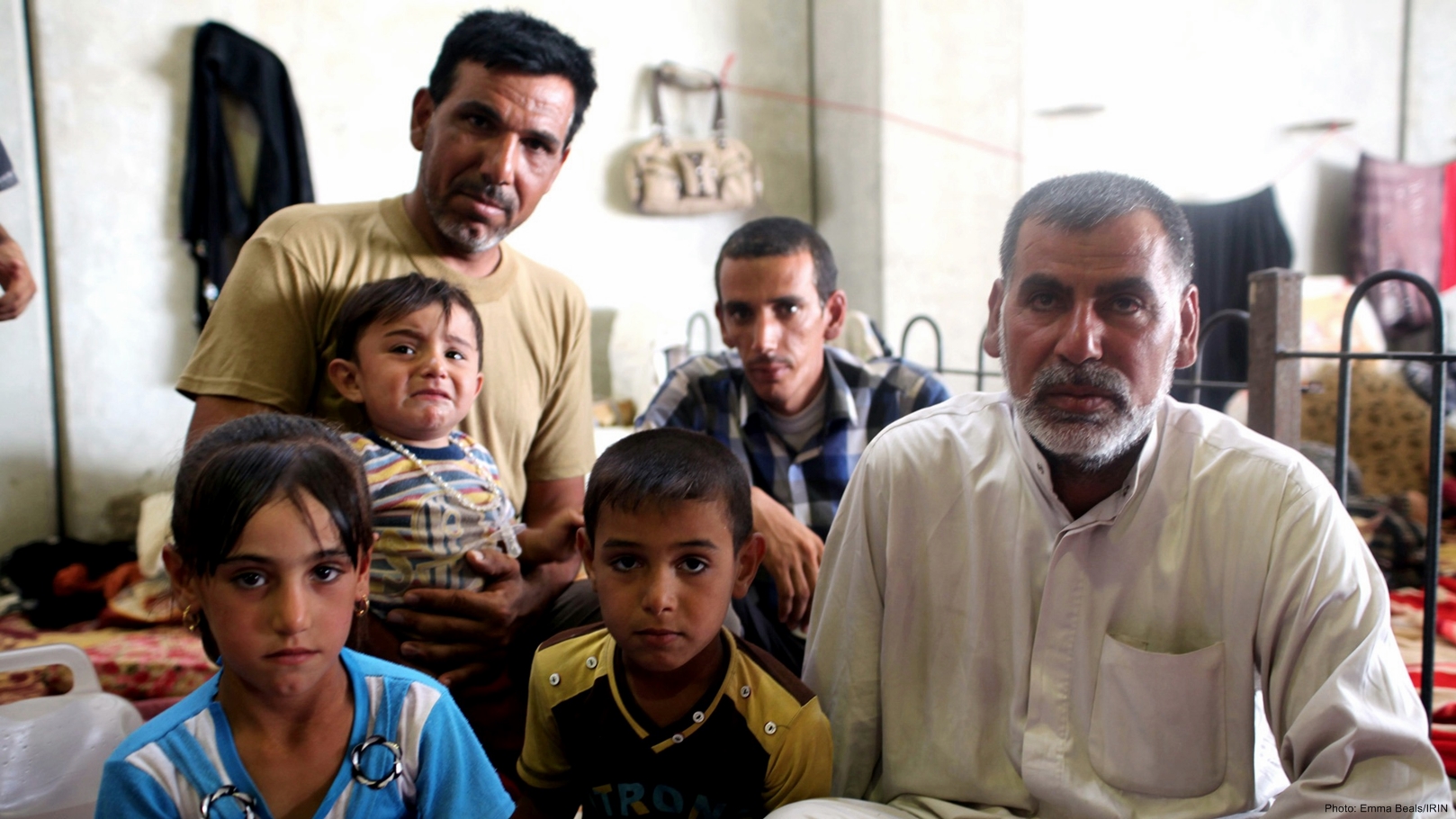
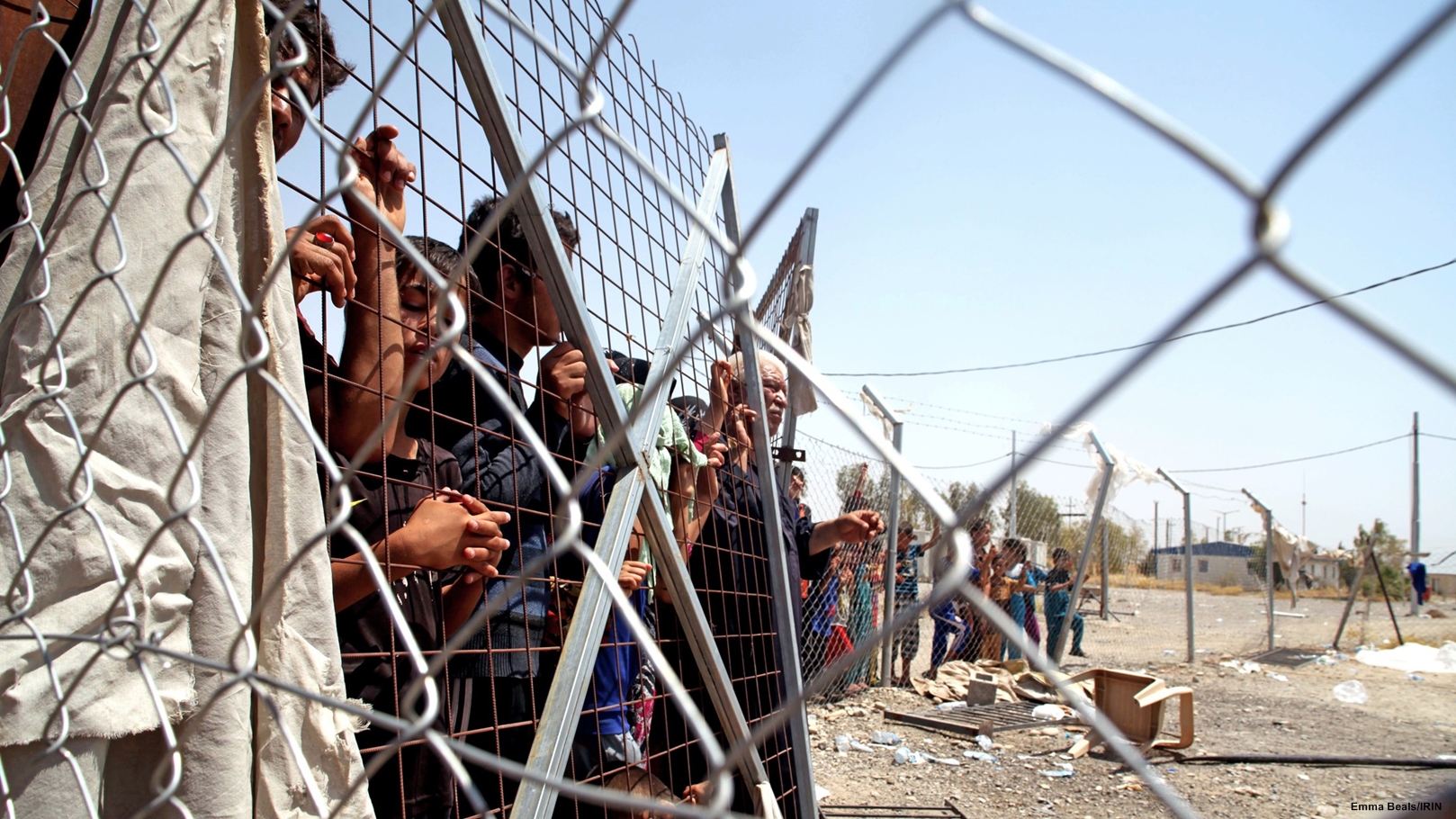
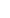
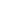
About 45 IDPs are now living in this open-fronted, half-built hotel building in the semi-autonomous Kurdish region of Iraq.
Highlights of the Updates in Iraq
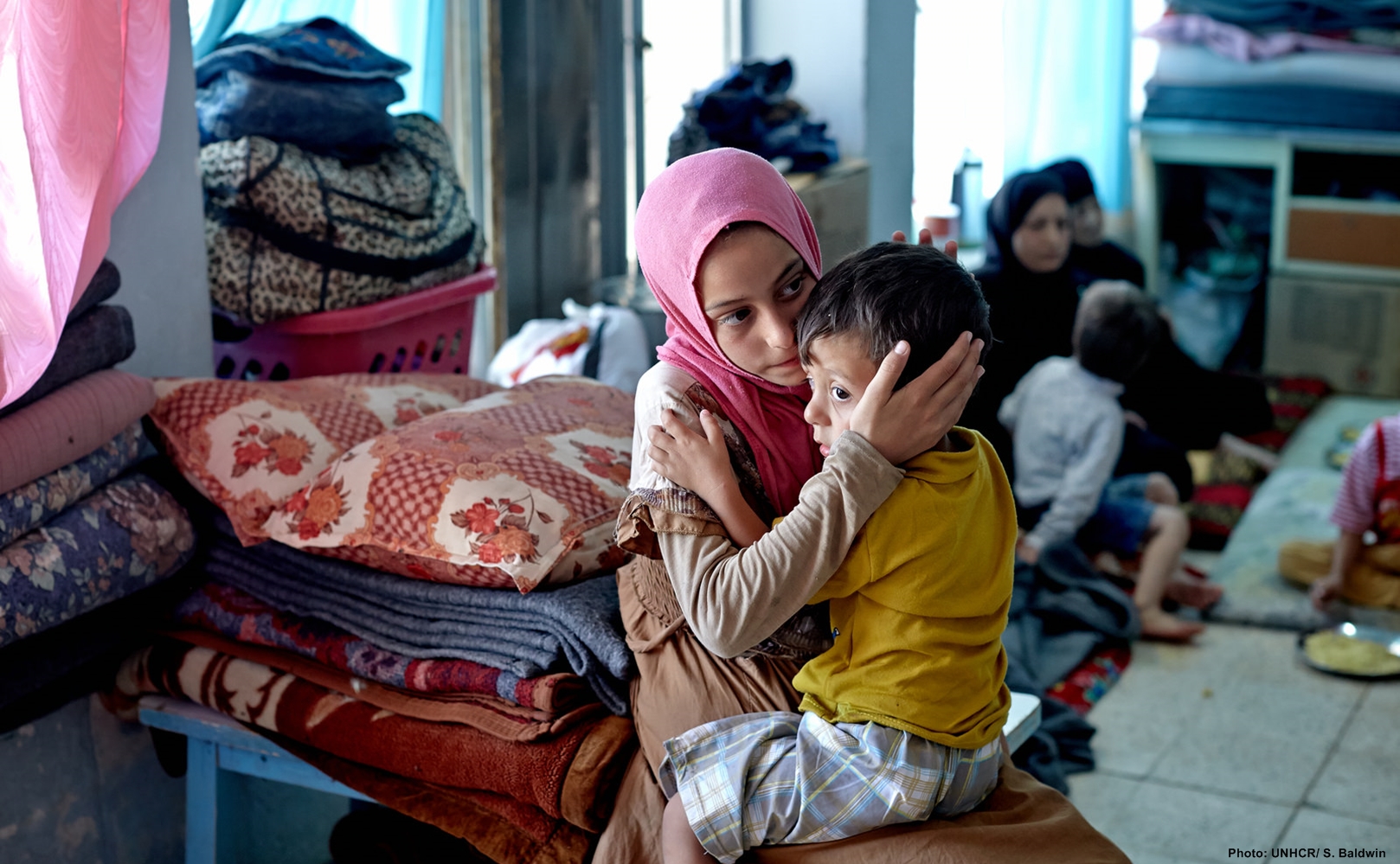
- Over 55,000 IDPs are reported to have crossed into Syria from Sinjar District, including many who were trapped on Sinjar Mountain. Most made their way back into Iraq through the Pesh Khabour checkpoint in the Kurdistan Region.
- Over 200,000 IDPs have entered Dahuk Governorate (Kurdistan Region) and are occupying schools, churches, mosques and unfinished buildings. Schools may not reopen on 10 September as scheduled, affecting over 850,000 children (Syrian refugees, Iraqi IDPs, Kurdish host community children).
- A water plant in eastern Mosul was partially destroyed by an airstrike, leaving large parts of the city without access to water. Food shortages are reportedly already occurring in Mosul as well. Millions of Iraqis may become severely food insecure later this year if these challenges are not resolved.
- The sub-district of Amirli, in Tooz district of Salah al-Din Governorate, has been surrounded by ISIS forces and completely inaccessible by road. An estimated 15,000 to 20,000 people reportedly remain inside Amirli, primarily Turkmen Shiites. The humanitarian situation there is said to be deteriorating quickly.
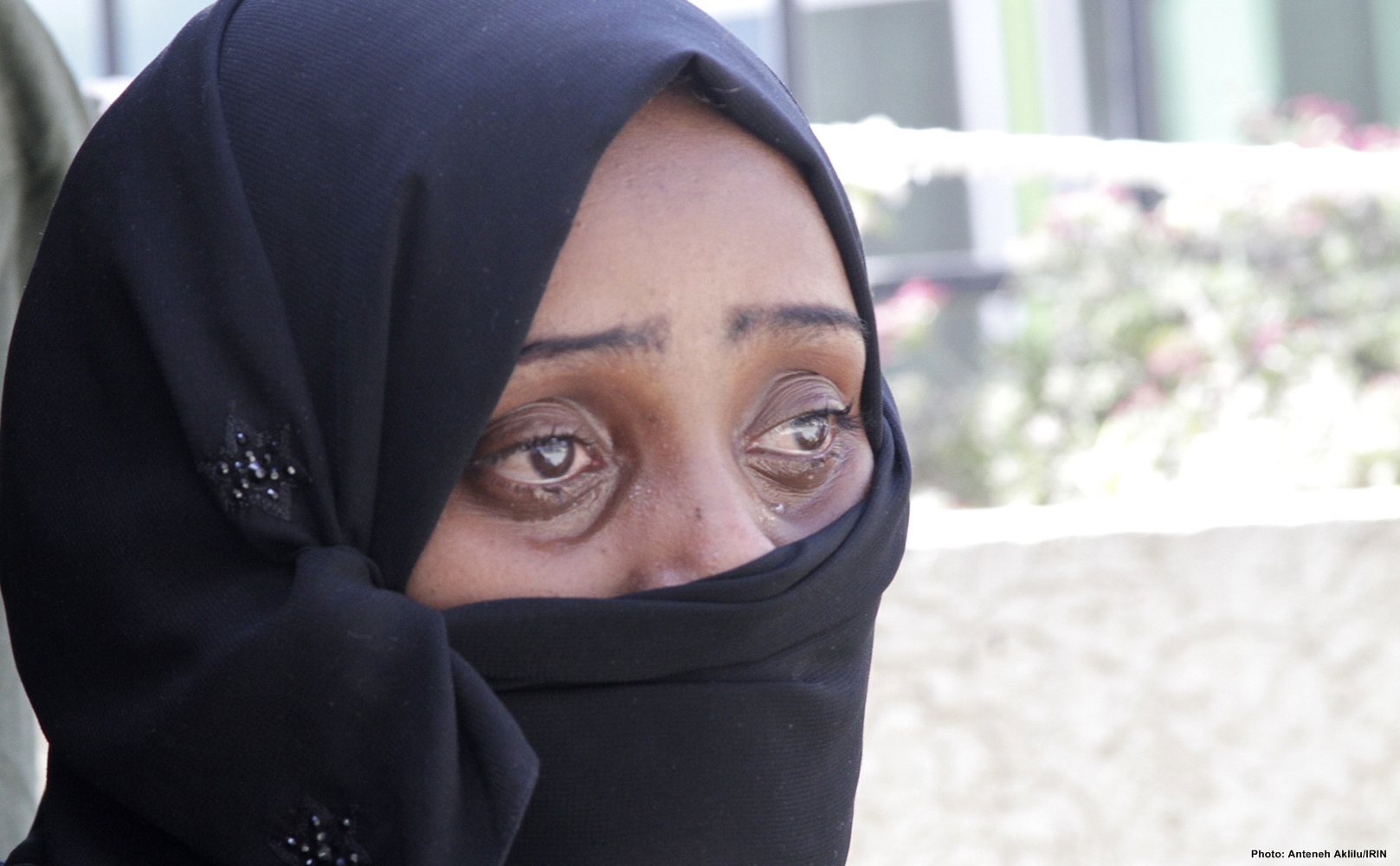
- There is mounting evidence that women belonging to the Yazidi and Christian religious minorities in Iraq are being raped and sold into slavery by the Islamic State (ISIS). One of the first to speak out was Vian Dakheel, the only Yazidi female MP, who addressed the Iraqi parliament in early August.
[Source: ReliefWeb(1), ReliefWeb(2), the Guardian]
Let’s Pray
- Ask God to stop the hand of those set on violence, bloodshed and intimidation in Iraq. Pray for the establishment of a lasting peace that all people groups will be accepted and protected.
- Pray for God’s protection to the minority ethnic and religious groups, especially the vulnerable children, women and elderly. Pray that those who are being raped and sold as slaves will be rescued soon.
- Pray for all those who have fled their homes and are living in fear and uncertainty. Ask God to keep them safe, provide for their needs and pour out His comfort and healing on all who are grieving.
- Thank God that tens of thousands of Iraqis were able to escape from Mount Sinjar, and pray for protection, provision and a rapid rescue for those who are still trapped.
- Lift up leaders in Iraq and around the world, praying that God will give them wisdom as they seek a solution to the crisis.